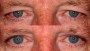
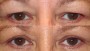
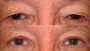
Upper Blepharoplasty
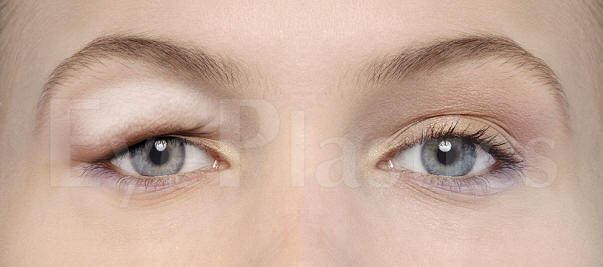
Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
Upper eyelid blepharoplasty is a surgical procedure that is capable of restoring vision as well as improving the appearance of your upper eyelids and involves the excision of excess upper eyelid skin, with or without orbital fat, for either functional or cosmetic indications.
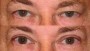
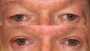
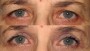
As we grow older, there is a tendency for developing apparent upper eyelid skin excess. The ageing upper eyelid, with crepe paper skin, ptotic fat, or both, is well known. The goal of upper eyelid blepharoplasty is to remove excess redundant tissue and re-contour the eyelids to achieve the desired results. The upper eyelid blepharoplasty is a mainstay of surgical rejuvenation of the orbital region.
Understanding Dermatochalasis
One of the primary causes of upper eyelid deformity is the ageing process which results in dermatochalasis. The combined effect of degenerative ageing process and pathological processes such as sun damage alter the skin and periorbital structures by reducing the number of collagen and elastic fibres in the dermis and atrophic changes in the epidermis, which is termed as dermatochalasis.
Gravity pulls down the fat and other orbital contents leading to a downward and forward displacement of orbital fat due to loss of septal and muscle support of the fat pads. It could also lead to weakness of the levator aponeurosis, and a consequent involutional ptosis. The loss of elasticity results in excess skin drooping over the underlying fat pads.
Indications for Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
Functional or Reconstructive Upper Blepharoplasty: This is indicated when the visual axis is obstructed by skin of the upper eyelids hanging across the eyelashes resulting in superior visual field loss. A functional blepharoplasty has three essential elements, namely:
- Patients must notice improvement in vision with skin elevation off their eyelids.
- A visual field test is used to document the loss of superior field of vision.
- Finally, photographic evidence to demonstrate upper eyelid skin laying across the eyelashes
Cosmetic Upper Blepharoplasty: This is done to accentuate and improve the appearance of the eyes. It is an elective surgery and is always done at the patient’s request. Cosmetic blepharoplasty will improve the patient’s looks, not the patient’s vision.
Good candidates for cosmetic blepharoplasty are:
- Patients with excess skin and fat on the upper eyelids having ‘tired-looking’ or ‘droopy’ eyes
- Patients with realistic expectations of the final outcome
Attainable intent for cosmetic blepharoplasty include:
- Improvement in upper eyelid symmetry
- Improvement of upper eyelid contour
Contraindications of Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
- Upper blepharoplasty is contraindicated in individuals seeking secondary gains or in individuals who have irrational expectations with surgery.
- A patient with multiple eyelid operations, lagophthalmos, and other general health issues should be handled with caution.
Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty – The Procedure
A blepharoplasty usually requires about 1 to 3 hours and could be done under local anaesthesia or under general anaesthesia.
An upper eyelid blepharoplasty involves the following steps:
Step 1. Local Anaesthesia: The procedure is done under local or modified local anaesthesia and patient co-operation is of utmost importance in achieving a symmetrical surgical outcome.
Step 2. Making the Skin Incision: Incision lines are made in the natural creases of the upper eyelids such that any resultant scar is camouflaged.
Step 3. Skin and Orbicularis Muscle Excision: The skin and orbicularis muscle are removed using Westcott scissors along the eyelid crease.
Step 4. Orbital Septum Excision: A strip of orbital septum is removed across the entire eyelid. This permits access to the eyelid fat pads beneath the orbital septum.
Step 5. Fat Removal: The eyelid is then re-contoured by a graded removal of the eyelid fat pad from different regions.
Step 6. Haemostasis: Aggressively control bleeding, particularly those arising from the orbicularis muscle.
Step 7. Closure: The wound is closed using either absorbable or non-absorbable sutures. Sutures should be removed at 7 to 8 days following surgery.
Blepharoplasty
When an advanced amount of upper eyelid skin is present, the skin could protrude over the eyelashes and causing a loss of peripheral vision. The outer and upper parts of the visual field are most commonly affected and the condition could cause difficulty with activities such as driving or reading. In this circumstance, upper eyelid blepharoplasty is performed to improve peripheral vision.
Risks and Complications of Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty
- Orbital haemorrhage, although rare, is the most dreaded complication of upper blepharoplasty and can result in blindness. Other complications include lagophthalmos, dry eyes, pain, swelling and stiffness of eyelids, scarring, ectropion, retinal detachment, infection, epiphora, and over-excision of eyelid tissues.
What can you expect from an Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty?
- After upper blepharoplasty, you can expect a visible reduction of bagging or drooping of eyelids. The upper eyelids are accentuated providing an aesthetically better and younger look. The aged look in the photo prior to the surgery is visibly changed in the photo taken after the surgery. It has a dramatic effect on the facial features giving the eyes a much younger and refreshed look. The eyes have a more distinctive appearance following blepharoplasty.
- However, it should be kept in mind that immediately after blepharoplasty, the skin appears red, irritated with minor bumpiness. These reduce gradually over time and your eyes which were dull and tired have a refreshed look.